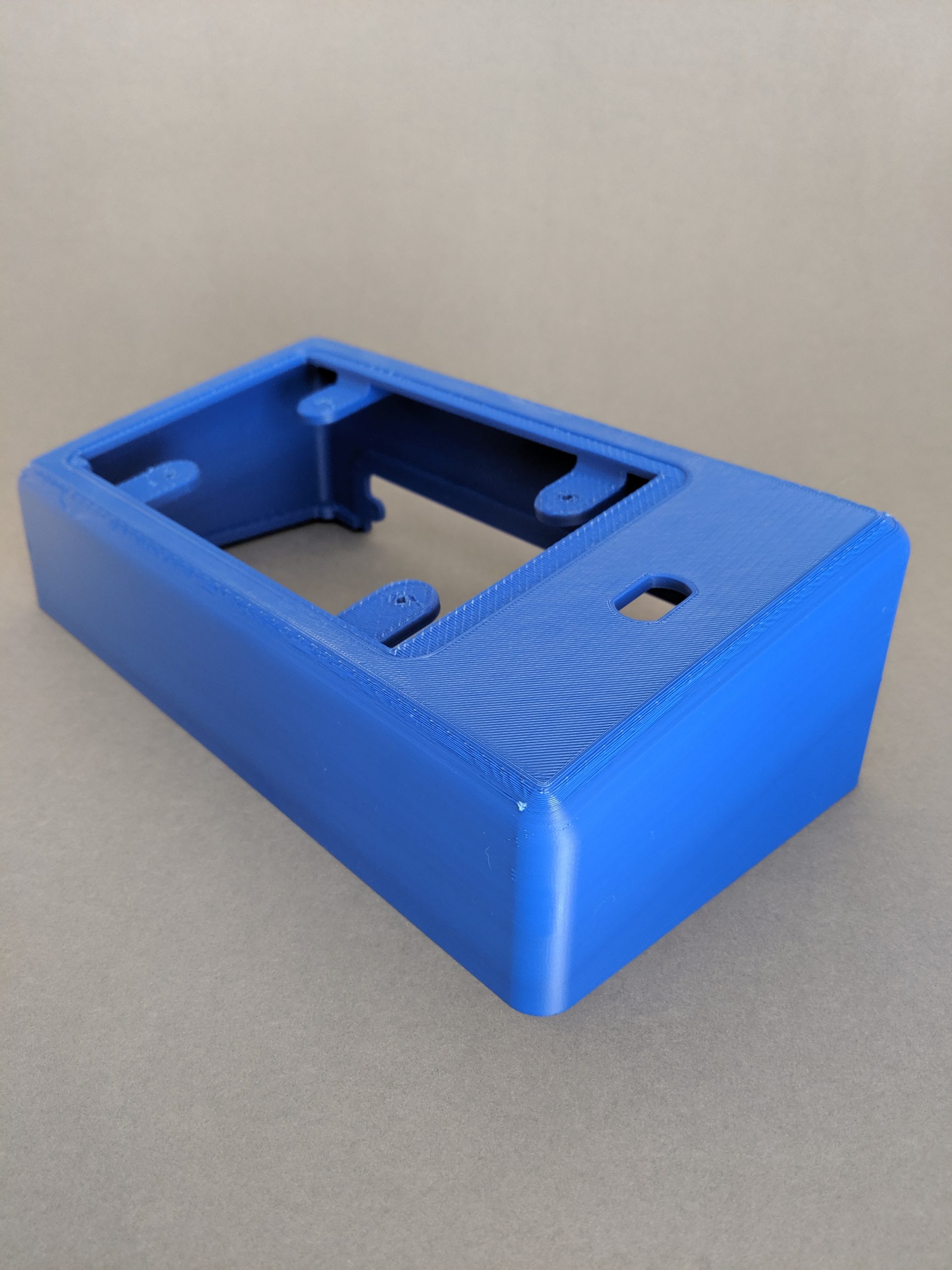
Looking for a cost-effective and time-saving manufacturing solution? Look no further than Thirty6’s 3D printing services. Our team of experts offers a wide range of materials, including PLA, ABS, ASA, HIPS, Nylon, Co-Polyesters, TPE, and composites like wood, brass, copper, and carbon fiber, to meet your specific needs. Our services are perfect for enclosures, jigs, physical prototypes, and end-use products.
One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is the ability to produce low volumes of products without the high initial setup costs of traditional manufacturing methods like injection molding. With Thirty6’s Micro Factory Manufacturing, we utilize multiple printers, often referred to as a “3D print farm,” to efficiently and cost-effectively produce your product in volume, making it an ideal solution for producing 1-1,000 pieces of a product.
3D printing is a great option for rapid prototyping, allowing you to quickly produce physical prototypes that can be tested and refined before committing to expensive tooling or mold-making processes. This can save you both time and money in the long run, while also ensuring your final product meets your exact specifications.
In addition to rapid prototyping, 3D printing is also an excellent choice for producing end-use parts and products. Our 3D printing services can help you produce high-quality, functional parts that meet your exact requirements, without the need for expensive tooling or molds.
At Thirty6, we pride ourselves on delivering high-quality results that meet our client’s specific needs. Contact us today to learn more about our 3D printing services and how they can help you reduce costs and improve your manufacturing processes.